In this lesson, you will learn how to write SELECT statements in SQL.
What is a SQL SELECT Statement?
The SELECT statement is the most commonly-used statement in the SQL programming language. It is the main statement that we used to retrieve data from a table within a database.
The SELECT statement is powerful because it can be combined with other statements that we will learn later in this course to return data that fits certain specified criteria.
Some example syntax for a SQL SELECT statement is below:
SELECT column_name FROM table_name;There are a few things worth mentioning from this example code:
- The actual SQL keywords (
SELECTandFROMare capitalized). While SQL code will still run if these words are not capitalized, it is considered a best practice to capitalize all of your SQL statements because it makes your name more readable. - The
column_nameandtable_namevariables are lowercase, which is also considered a best practice. - The statement ends with the
;character, which tells SQL that the statement is finished.
The * Wildcard Character
In SQL, the * character is used as a wildcard character. It is used to generate all of the potential variables that could fill a statement. As an example, you can select all of the columns from the film table using the following SQL statement:
SELECT * FROM film;While the * character does have its uses, it is not always a good option for retrieving data. This is because many SQL databases are very, very large, and using the * character will create unnecessary traffic between the database server and the application you're using to query it (in this case, pgAdmin4).
Using The SQL SELECT Statement With Multiple Columns
It is possible to select multiple columns from a database table using the SQL SELECT statement. To do this, you need to separate the column names with commas like this:
SELECT column_name1, column_name2 FROM table_name;The columns will be listed in the order that you present them in the SELECT statement.
A real example of this using our DVD Rental database is below:
SELECT title, description FROM film;Here is what the output of this statement looks like in pgAdmin:
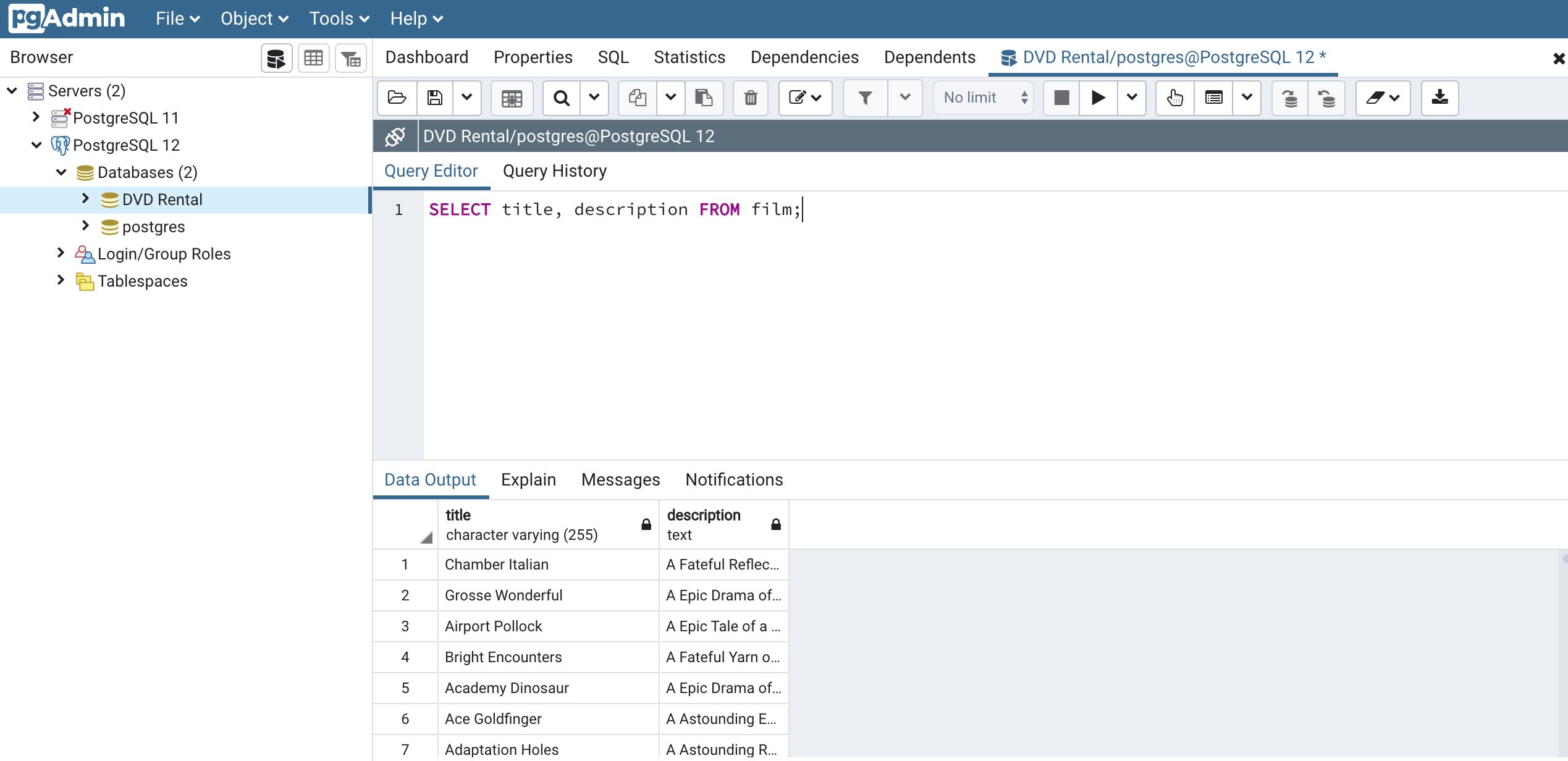
Final Thoughts
In this lesson, you received your first introduction to writing SQL queries with the SELECT statement. In the next section we will learn how we can pair the SELECT statement with the DISTINCT keyword to eliminate duplicate rows from a column in a SQL database.
