In this lesson ,you will learn how to use the SQL LIMIT clause.
What is the SQL LIMIT Clause?
The SQL LIMIT clause allows us to limit the number of rows that are returned from a SQL query. It is useful if you only want to see a few rows from the database table to get a rough idea of what the table's layout is.
You can also use the LIMIT clause if you only need to see the data points that lie at the extremes of a data distribution, which can be done by pairing the LIMIT clause with the ORDER BY statement.
The LIMIT clause goes at the very end of a SQL query. This makes sense, because its operations (eliminated all but a certain number of rows) needs to be done after all other data manipulation.
Here is a generalized example of how the LIMIT clause fits into a SQL query:
SELECT column_name
FROM table_name
LIMIT number;Combining the LIMIT Clause with the ORDER BY Statement
As mentioned, combining the LIMIT clause with the ORDER BY statement is a very powerful tool for generating database rows that have extreme values for a particular column.
As an example, here is the generalized syntax for returning the 5 rows that have the highest value for column_name:
SELECT *
FROM table_name
ORDER BY column_name DESC
LIMIT 5;Let's apply this technique to our DVD Rental database. More specifically, let's identify the 10 movie titles with the longest movie length.
To do this, let's start with a generic SELECT statement. We will be working with the film table:
SELECT *
FROM film;Next, let's add our ORDER BY statement. The column that we want to order by is length, and since we want the movies with the longest length, we will use the DESC keyword:
SELECT *
FROM film
ORDER BY length DESC;The last step is to add the LIMIT clause:
SELECT *
FROM film
ORDER BY length DESC
LIMIT 10;Here's what the output looks like:
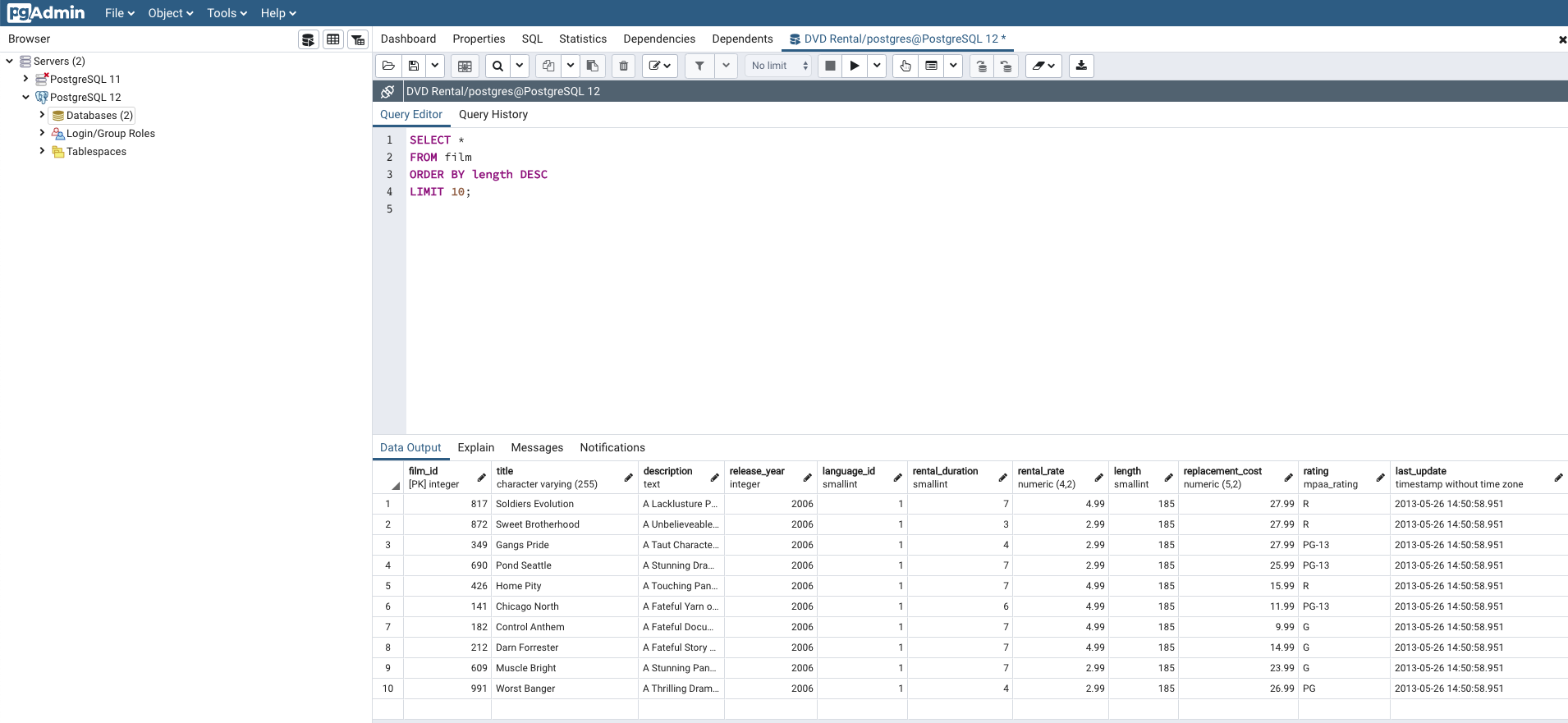
If you wanted to only get a list of the titles from the longest movies in the database, you could do so by replacing the wildcard character * with the title column name, like this:
SELECT title
FROM film
ORDER BY length DESC
LIMIT 10;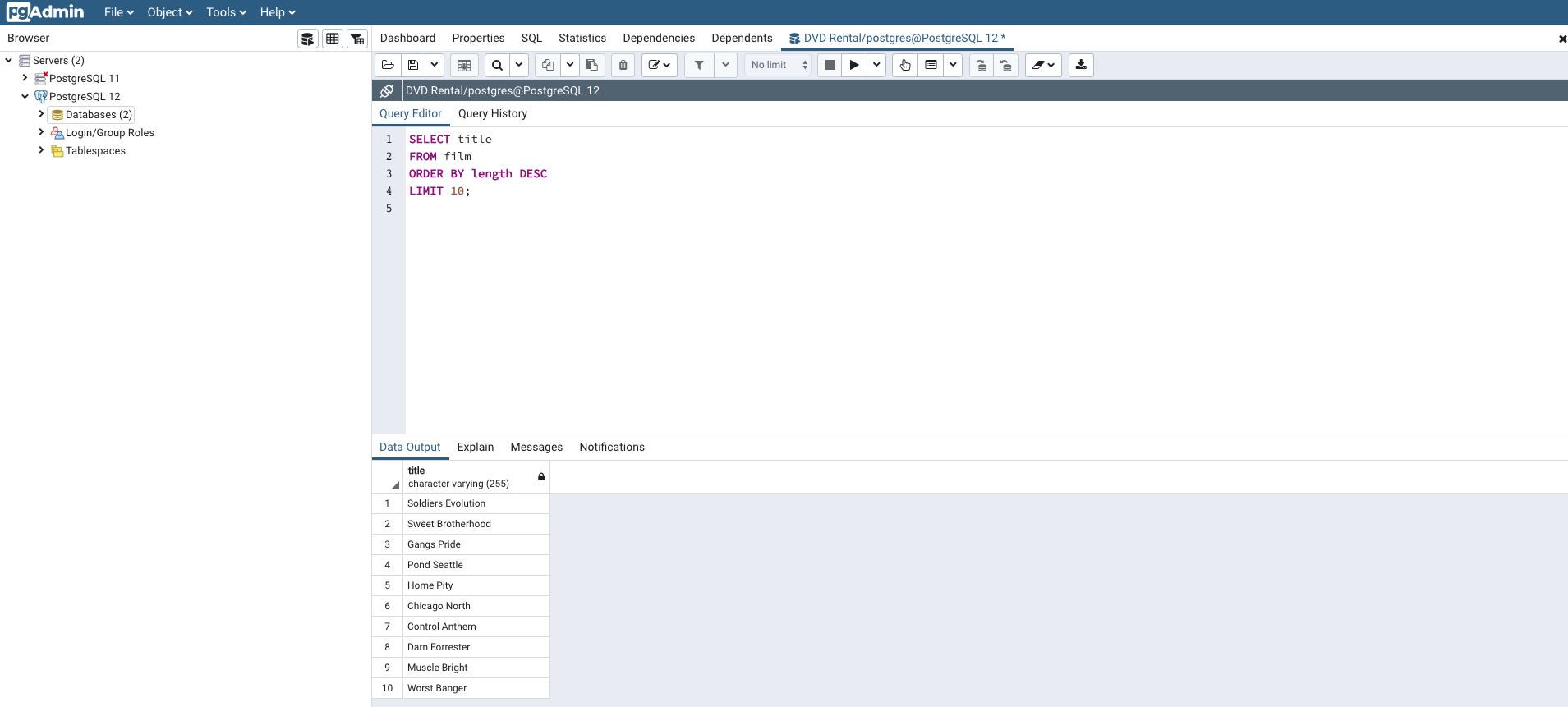
Final Thoughts
In this lesson, you learned how to use the SQL LIMIT clause to restrict the number of rows that are returned by a SQL query.
In the next lesson, I will show you how to use the BETWEEN statement, which is similar to chaining together multiple WHERE statements but is a bit more readable.
