How to Write a Bubble Sort Algorithm in Python
Python is a versatile and robust programming language. While it is better known for its prowess in AI and Machine Learning applications, Python can be used for many other programming tasks.
Sorting functions are an important aspect of all programming languages. Python provides its own sorting function based on the Timsort, which is a hybrid stable algorithm derived from Merge Sort and Insertion Sort. However, this may not be sufficient for all programming needs, and it is always an advantage to be knowledgeable about implementing other sorting algorithms.
Despite an abundance of sorting algorithms, there is no one algorithm that suits all sorting needs. Especially with the exponential growth of data science, being knowledgeable about many algorithms helps greatly.
Bubble sort is one of the most straightforward sorting algorithms. The basic idea is that a given list or sequence of data is verified for the order of neighboring elements by comparing them with each other. Elements are swapped if the order does not match the expected result. For example, if the expected result is a sorted list in the ascending order, once the comparison is performed, if the first element is greater than the second, they are swapped.
Table of Contents
You can skip to a specific section of this Python bubble sort tutorial using the table of contents below:
- How Does A Bubble Sort Algorithm Work?
- Implementation in Python
- Time and Space Complexities
- Final Thoughts
How Does A Bubble Sort Algorithm Work?
Let’s take a look at a visual example of bubble sort before divinginto its technicalities. Consider the following array.

Now, let’s try to sort this array from the smallest to largest using bubble sort. Let's start with the first element, 78. The yellow highlights are used to indicate the elements being considered.

Let’s compare 78 with its immediate neighbo- 27:

As 78 is greater than 27, they need to be swapped.

Now let's consider 78 with its next immediate neighbor.

They are already in the correct order because 78 is smaller than 81. This means that they do not need to be swapped. So the algorithm will proceed.

Let’s consider 81 with its immediate neighbor 14.

81 is greater than 14. So they need to be swapped.

Now let's consider 81 and its immediate neighbor - 71.

They need to be swapped because 81 is greater than 71.
Let’s consider what we can observe after the first iteration:
- The array is still not fully sorted (Eg: 78 > 14).
- The array needs to be sorted further through one or more iterations.
- The largest element of the array has been placed inits correct position, sowe can say that the position with the highest index is sorted. Therefore, from the next iteration, we have to consider only four elements.
Let’s do one more iteration of sorting. The Green highlights are used to indicate elements that are already sorted.
Let us start with the first element 27.

Let's compare 27 with its immediate neighbor, 78. There is no need for swapping because they are already in the correct order.

Let’s proceed. Now consider 78 with its neighbor, 14.

Because14 is smaller than 78, they need to be swapped.

Now let’s consider the next element, again it’s 78. Let’s compare it with its new neighbor, 71.

Because 78 is greater than 71, they need to be swapped.

After the first iteration, 81 was placed into the correct position and now, after the 2nd iteration, 78 has been placed correctly.

We can draw a few more conclusions with this new information. With each iteration, the largest number of the considered portion of the array is sorted into its correct position.
We can also understand one more thing. The largest elements tend to move to the far-right corner with each iteration, similar to how a bubble inside a carbonated drink rises to the surface. Thus its name - bubble sort.
Let’s now sort the array with the remaining iterations:
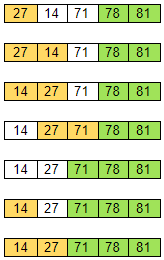
At this point, because there is only one unsorted element left, the array is considered sorted. Therefore, we do not need to compare it with another element. So we can say that if there are n number of items, we only need to perform n-1 iterations of traversing through the unsorted portion of the array.
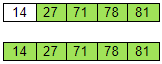
There is it. That is how the bubble sort algorithm works. Now let’s try to implement the code in Python.
Implementation in Python
Let’s recall what we did earlier. We did two main things while sorting the array in the ascending order.
- We traversed through the array one time, comparing elements with their immediate neighbor element. We can call this one iteration. At each successive iteration, we only had to consider one less item as the far-right end of the array was being sorted.
- If we had n items, we repeated this iteration for n-1 times altogether to produce a sorted array.
Considering the above, we can understand that we need nested for loops for the following two tasks.
- To traverse through the elements of the array performing iterations n-1 times.
- To compare elements and swap them if they are not in order.
In Python, we have lists instead of arrays. So, let's call them lists from now on.
- Let’s start by defining a list of random numbers.
my_list = [34, 76, 90, 12, 32, 44, 55]
-
Assign the number of elements in our list to the variable n and implement a for loop to traverse through the list n-1 times.
n = len(my_list)
for i in range(n-1):
* Write a nested for loop inside the outer loop that was created above. This is to compare elements and swap them where needed.
```python
for j in range(0, n-1):The largest element of the unsorted elements reaches its rightful position on the right side of the list. So we can optimize the nested for loop as follows:
for j in range(0, n-1-i):- Now let's write the code to make comparisons and swap the values of elements when an element is greater than the one next to it.
if(my_list [j] > my_list [j+1]) :
temp_val = my_list[j]
my_list[j] = my_list[j+1]
my_list[j+1] = temp_valPython allows us to optimize the above comparison code as follows:
if(my_list[j] > my_list[j+1]):
my_list[j], my_list[j+1] = my_list[j+1], my_list[j]- Now that the iteration and comparison is done, let’s print the sorted list.
print(my_list)The complete code is given below. The iteration and comparison code has been added to a function to facilitate reusability.
##The complete code
def bubble_sort(my_list):
n = len(my_list)
fori in range(n-1):
forj in range(0, n-1-i):
if(my_list[j] > my_list[j+1]):
my_list[j], my_list[j+1] = my_list[j+1], my_list[j]
return my_list
unsorted_list = [34, 76, 90, 12, 32, 44, 55]
sorted_list = bubble_sort(unsorted_list)
print(sorted_list)Time and Space Complexities
Time and space complexities are the usual measurements of how good an algorithm is. They can be used to interpret the performance of an algorithm quantitatively.
Time complexity, which is more significant, is considered for the best, average, and worst cases. Bubble sort has two for loops, with one nested within the other,running from 0 – n approximately. We can consider the time complexity as O(n2). However, considering the best case which is when the list or the array is sorted, the complexity becomes O(n) as it only has to run n-1 times.
Considering the average case and the worst case, which is when the list is inverted, the time complexity holds to O(n2).
Final Thoughts
Bubble sort is a very simple algorithm and is considered to be the stepping stone of sorting algorithms. It is sometimes used to sort almost-sorted arrays to perform tasks in O(n).
The following is a summary of the complexities of bubble sort.
|
Time Complexity |
Space Complexity |
||
|
Best |
Average |
Worse |
All Cases |
|
O(n) |
O(n2) |
O(n2) |
O(1) |
Have a good day!
