In this lesson, we will learn how to concatenate pandas DataFrames. This will be a brief lesson, but it is an important concept nonetheless. Let's dig in!
The DataFrames We'll Use In This Lesson
To demonstrate how to merge pandas DataFrames, I will be using the following 3 example DataFrames:
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3'],
'D': ['D0', 'D1', 'D2', 'D3']},
index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7'],
'C': ['C4', 'C5', 'C6', 'C7'],
'D': ['D4', 'D5', 'D6', 'D7']},
index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
df3 = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['A8', 'A9', 'A10', 'A11'],
'B': ['B8', 'B9', 'B10', 'B11'],
'C': ['C8', 'C9', 'C10', 'C11'],
'D': ['D8', 'D9', 'D10', 'D11']},
index=[8, 9, 10, 11])How To Concatenate Pandas DataFrames
Anyone who has taken my Introduction to Python course will remember that string concatenation means adding one string to the end of another string. An example of string concatenation is below.
str1 = "Hello "
str2 = "World!"
str1 + str2
#Returns 'Hello World!'DataFrame concatenation is quite similar. It means adding one DataFrame to the end of another DataFrame.
In order for us to perform string concatenation, we should have two DataFrames with the same columns. An example is below:
pd.concat([df1, df2, df3])
By default, pandas will concatenate along axis=0, which means that its adding rows, not columns.
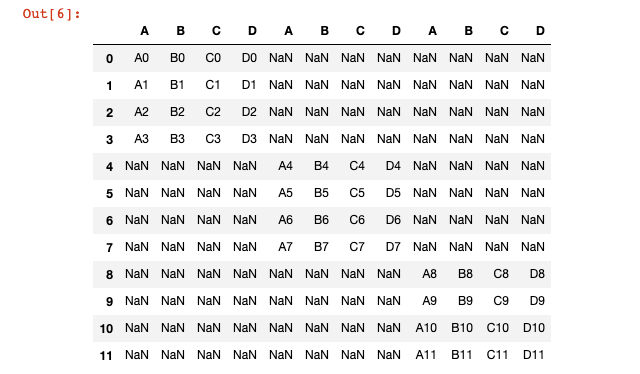
If you want to add rows, simply pass in axis=0 as a new variable into the concat function.
pd.concat([df1,df2,df3],axis=1)In our case, this creates a very ugly DataFrame with many missing values:
Moving On
That concludes our brief discussion of DataFrame concatenation. Let's dig into some practice problems next!
